Overview
Redpoint Data Management (RPDM) employs a specific approach to handling NULL and empty values across different data types. RPDM provides flexibility in handling NULL values while ensuring compatibility with SQL-based operations. Understanding how NULL values are processed across different data types helps in configuring data management workflows effectively. This document outlines how RPDM represents and processes NULL values, including key differences from SQL databases.
NULL representation in RPDM
RPDM supports NULL values across all data types, but its behavior varies between text and non-text data types.
For textual data types:
-
TextVar -
TextFixed -
Unicode
and only for those types, the empty string and the NULL value are one and the same, and indistinguishable in RPDM. However, for all other types, there is no analogous “empty” value; therefore, displaying <<NULL>> for NULL non-text values and blank for other types helps to emphasize the distinction. Note that this is only for display in the Data Viewer.
The <<ERROR>> value in RPDM is automatically converted to NULL in databases, which typically have no such representation.
Text data types
-
RPDM does not distinguish between NULL and empty strings.
-
The system treats both as equivalent, displaying nothing in the Data Viewer.
-
An explicit distinction is only made when inserting into SQL databases, using the Treat empty text as null when loading option.
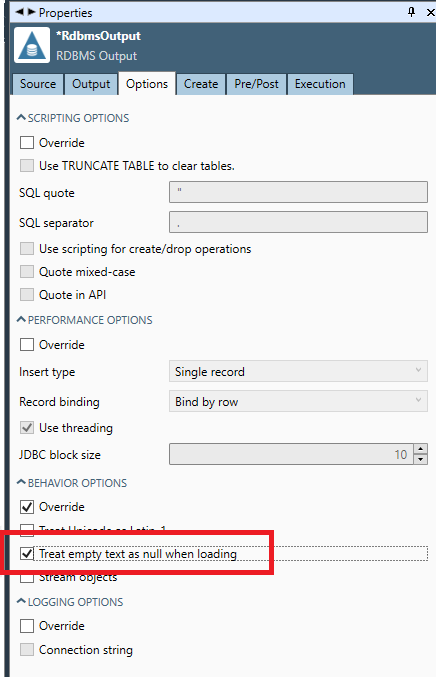
Non-text data types
-
RPDM explicitly represents NULL values for all non-text data types.
-
Even binary types differentiate between NULL and zero-length values, unlike some SQL databases.
-
The Data Viewer displays
<<NULL>>for NULL values in non-text data types.
Sources of NULL values
A NULL value in RPDM can arise in several ways:
-
Blank or NULL data imported from external sources.
-
A string operation that results in an empty string.
-
Conversion of an empty string to another data type.
NULL handling in key queries and operations
Unlike SQL, where NULL represents a non-value, RPDM treats NULL as a distinct value. This has implications for key operations:
-
Joins and Comparisons: NULL values can be used in joins and equality tests like any other value.
-
Key-Based Queries:
-
In
RdbmsInputkey queries andRdbmsOutputdelete/insert operations using keys, NULL values are treated as regular values. -
The system ensures that NULL key values can be used to locate records with NULL key columns.
-
-
Distinguishing NULL from Empty Strings:
-
When performing key-based queries, users must decide whether NULL and empty text keys should be treated as distinct or equivalent.
-
This is controlled via the same Treat empty text as null when loading option.
-
There is no built-in mechanism to simultaneously search for both NULL and empty strings in key-based queries.
-

