For textual file formats such as flat, CSV, JSON, or XML files, Data Management can analyze a sample of the records and identify schema elements. Depending on the file format, these may include field name, field type, field delimiter and qualifier, field size, and code page.
To analyze the schema of a file:
-
Specify the Input file or Output file on the Configuration tab of the tool's Properties pane.
-
Select Analyze

-
Examine the Data type grid:
-
Select or clear Allow to allow a data type to be considered in the analysis. If neither Unicode nor TextVar are selected, the default data type (Unicode) will be used in analysis.
-
Set the Minimum size for sized data types, or accept the default values.
-
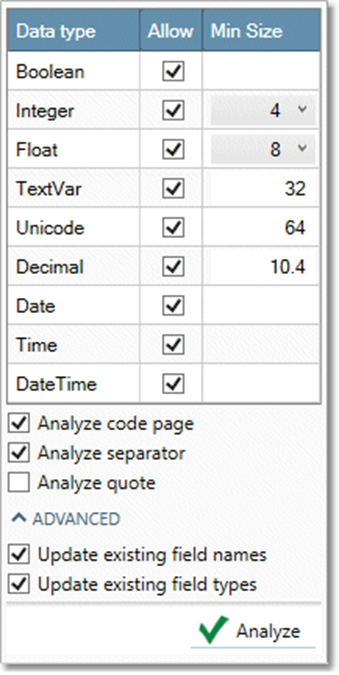
-
Configure analysis options, or accept the default settings.
|
Option |
Tool |
Action |
|---|---|---|
|
Analyze code page |
CSV Input |
Identify the code page. |
|
Analyze separator |
CSV Input, CSV Direct |
Identify the characters used to separate (delimit) fields. |
|
Analyze quote |
CSV Input, CSV Direct |
Identify the characters used to quote (escape) the data. |
|
Add new fields |
CSV Direct, XML Input, XML2 Input and Output, JSON Input and Output |
Add new fields. |
|
Remove missing fields |
CSV Direct, XML Input, XML2 Input and Output, JSON Input and Output |
Remove fields no longer present. |
|
Update existing field names |
CSV Input, XML2 Input and Output |
Update field names. |
|
Update existing field types |
CSV Input, CSV Direct, XML Input, XML2 Input and Output, JSON Input and Output |
Update data types of existing fields. |
|
Use long field names |
JSON Input and Output, XML2 Input and Output |
Prepend the parent path structure to field names. Nested substructure will produce field names with a prefix that includes the outer keys. This does not apply to JSON arrays or XML repeated elements, because they will get their own child record types. |
-
Select Analyze to start the analysis.

