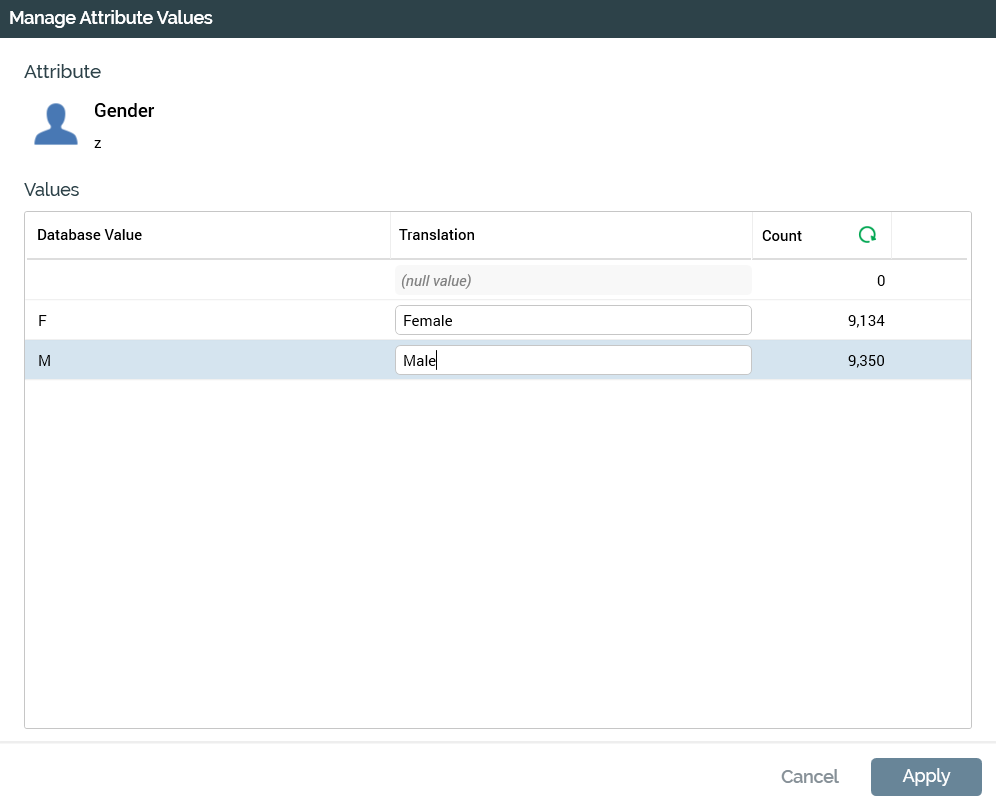
Management of an attribute’s translation values is carried out in the Manage Attribute Values modal dialog.
Translations are used when configuring list comparison criteria. If a translation exists for an attribute value, it is displayed instead of its database equivalent when building a list criterion.
An attribute’s distinct values are listed alphabetically by database value within the dialog. The most frequently occurring values are listed (up to a maximum number of values as defined by a system configuration setting (AttributeValueListSize)). If all values are not listed, a warning message is displayed.
You can provide a string translation for each displayed value. The translation may be a maximum of 100 characters. Attribute translations are specific to an attribute—translation values are not shared across database column attributes that share the same underlying database column. If you delete a translation the value reverts to the original database value.
A “Null value” entry is always shown in the list. You cannot manage this value’s translation.
You can retrieve the latest attribute values and counts from the data warehouse or an auxiliary database by selecting the button shown in the Count column header. Any new values are added to the list (if permissible according to the number of values displayed in the list). When you do so, by default, new values’ Translations are set to the Database Value. Any existing translations are retained where the relevant rows are still present. This applies even if a translation had been provided in the past for a value that was no longer present at the point of refresh.
Note that you cannot manage values for decimal, money, date, parameter, exists in table, model project, parameter or map item attributes.
Note also that managed values are not output in export files generated from RPI. In such circumstances, raw data values are always output.

