If you’re viewing this topic from within the Redpoint Service Desk Portal, some diagrams may not render correctly. Please view this topic on the Redpoint Docs site instead.
Overview
The following guide shows the capabilities of SendGrid within Redpoint Interaction, how sending emails/synchronizing state data works, and links to other resources.
Key capabilities
The SendGrid connector provides the following key capabilities:
-
Channel Configuration
-
The ability to send emails via an Interaction using an Offer Activity and Queue Listener
-
Receiving state/disposition data via the Channel Synchronization Task
-
Using state/disposition data as inputs to additional workflows and downstream activities
Unique features
The SendGrid connector supports the following features:
-
Timely processing of state/disposition data via their webhook functionality
-
Support for using External Content Providers such as Amazon S3 and Azure Storage for ingesting event files via the Callback Service
-
Ideal platform to use for Queue Listeners as they support timely delivery of emails
-
Support for BCC within the channel configuration
-
The ability to tag emails for reporting purposes by utilizing campaign categories at the channel level (more details available on this page)
-
The ability to include List Unsubscribes in the email header, supporting both email and web page unsubscribes (more details available on this page)
-
Various channel configuration options to optimize performance for outbound and inbound processing
-
The ability to save Event and Mail Merge files for auditing purposes or utilizing those files for an external process
-
Enhanced security with the option to add a secondary password for all requests to their APIs
-
The ability to support custom headers at the channel level (more details and use cases available on this page)
Process flow
The following flow chart shows how the SendGrid channel works within both outbound fulfillment and inbound state synchronization.
Outbound processing
Inbound processing
Outbound fulfillment
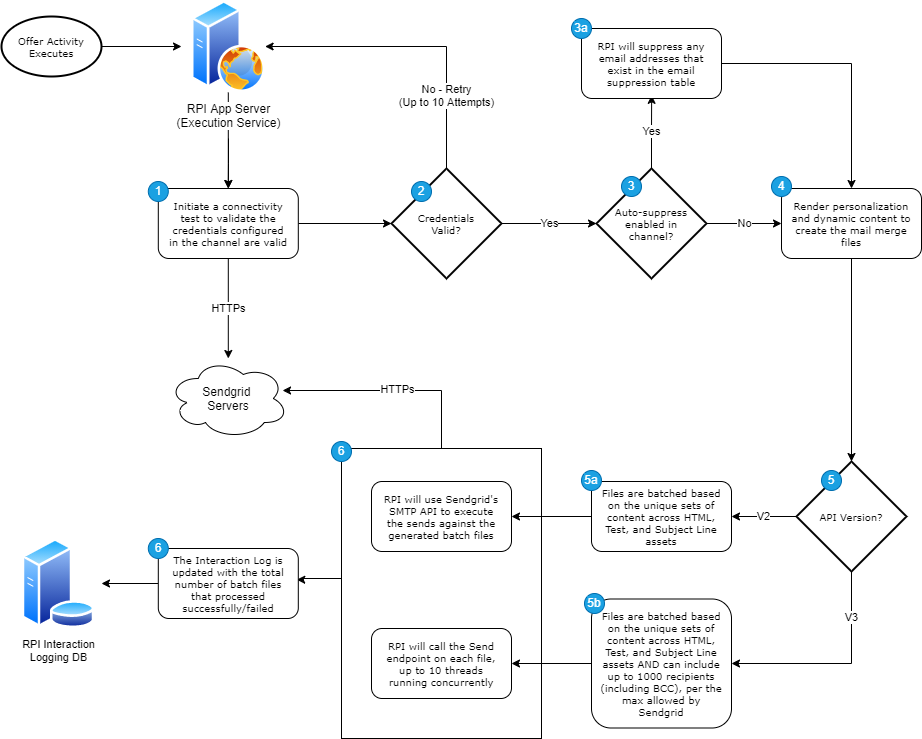
The SendGrid connector performs the following steps when it is used as part of an outbound Offer Activity. Both V2 and V3 APIs are listed in the steps below.
Step 1
Initiate a connectivity test to validate the credentials configured in the channel are valid.
The following are the V2 APIs:
Method
GET
Endpoint
https://api.sendgrid.com/api/profile.get.json?api_user=<user_name>&api_key=<sendgrid_password>
Request Body
None
Response Body
[
{
"username": "<user_name>",
"email": "<account_email>",
"active": "true",
"first_name": "",
"last_name": "",
"address": "34 Washington St",
"address2": "",
"city": "Wellesley",
"state": "MA",
"zip": "02481",
"country": "US",
"phone": "",
"website": "",
"website_access": "true"
}
]
The following are the v3 APIs:
Method
GET
Endpoint
https://api.sendgrid.com/v3/api_keys
Request Body
N/A
Response Body
{
"result": [
{
"name": "redpoint_qa",
"api_key_id": "TYWaXbJYSdm3fX_6xEuELg"
}
]
}
Step 2
If the connectivity fails, it will retry up to 10 attempts.
Step 3
If the channel is configured to auto-suppress unsubscribes, RPI will query the suppression email table to identify and suppress any matching email addresses before generating the mail merge files.
Step 4
Use the Razor templating engine to render personalization and dynamic content to create the mail merge files.
Step 5a
Files are batched based on the unique sets of content across HTML, Test, and Subject Line assets.
Step 5b
Files are batched based on the unique sets of content across HTML, Test, and Subject Line assets.
AND
Each batch file includes up to 1000 recipients (including BCC), per the max allowed by SendGrid.
Using the v3 API may create additional batch files if each unique set of content includes more than 1000 recipients (including BCC, if configured).
Step 6
RPI will loop through each of the files and initiate the send to SendGrid.
The following are the V3 APIs:
Method
POST
Endpoint
https://api.sendgrid.com/v3/mail/send
Request Body
See attached file sendgrid_send_example.json
Response Body
None
Step 7
Once the sends are complete, the Interaction Log is updated with the total number of batch files that processed successfully/failed.
For example, the attached file is from a log that sent 11K emails: Sendgrid_Interaction_Log.txt
State data synchronization
SendGrid callback service
To set up either the Standard or Web API callback service, the following prerequisites must exist:
-
A public-facing web server (installing on the same VM as RPI is NOT recommended)
-
A SendGrid callback service website, hosted in IIS
Installing and configuring the SendGrid Callback Service
The SendGrid Callback Service is a separately installed web service that is designed to listen, and react, to state update events coming from SendGrid.
More information on installing and upgrading the Callback Service can be found in the following pages of the RPI Admin Guide
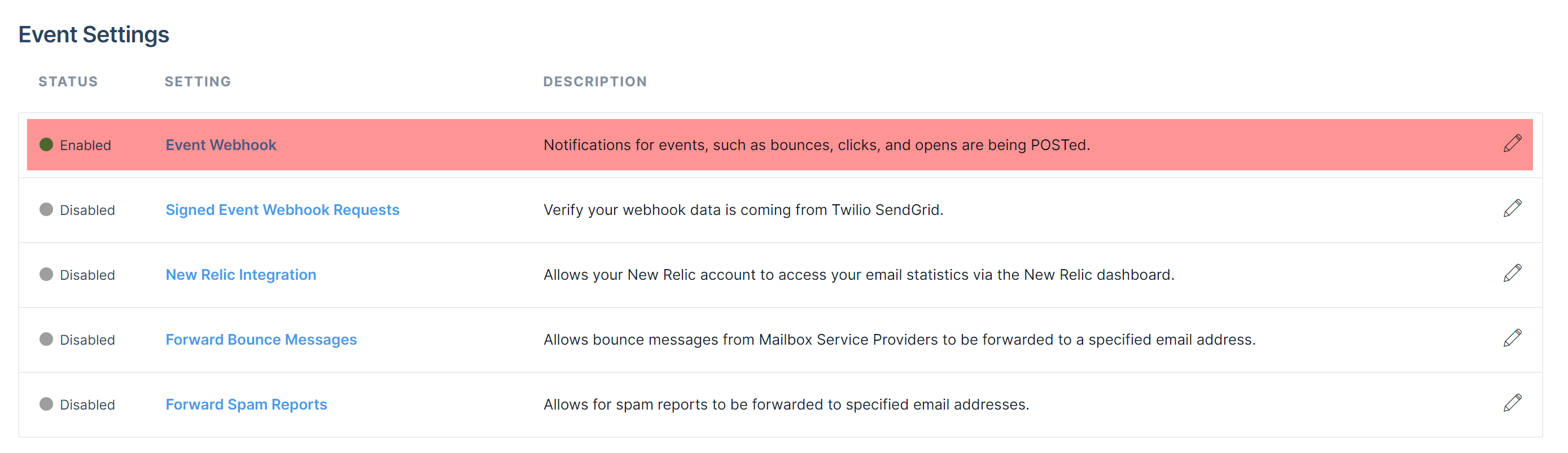
To configure the web hook URL in the SendGrid portal:
-
Once the callback service is configured on the web server, the web hook URL must be configured within the SendGrid portal, under Settings>Mail Settings>Event Webhook:
-
When you select the edit icon, the configuration page will open:
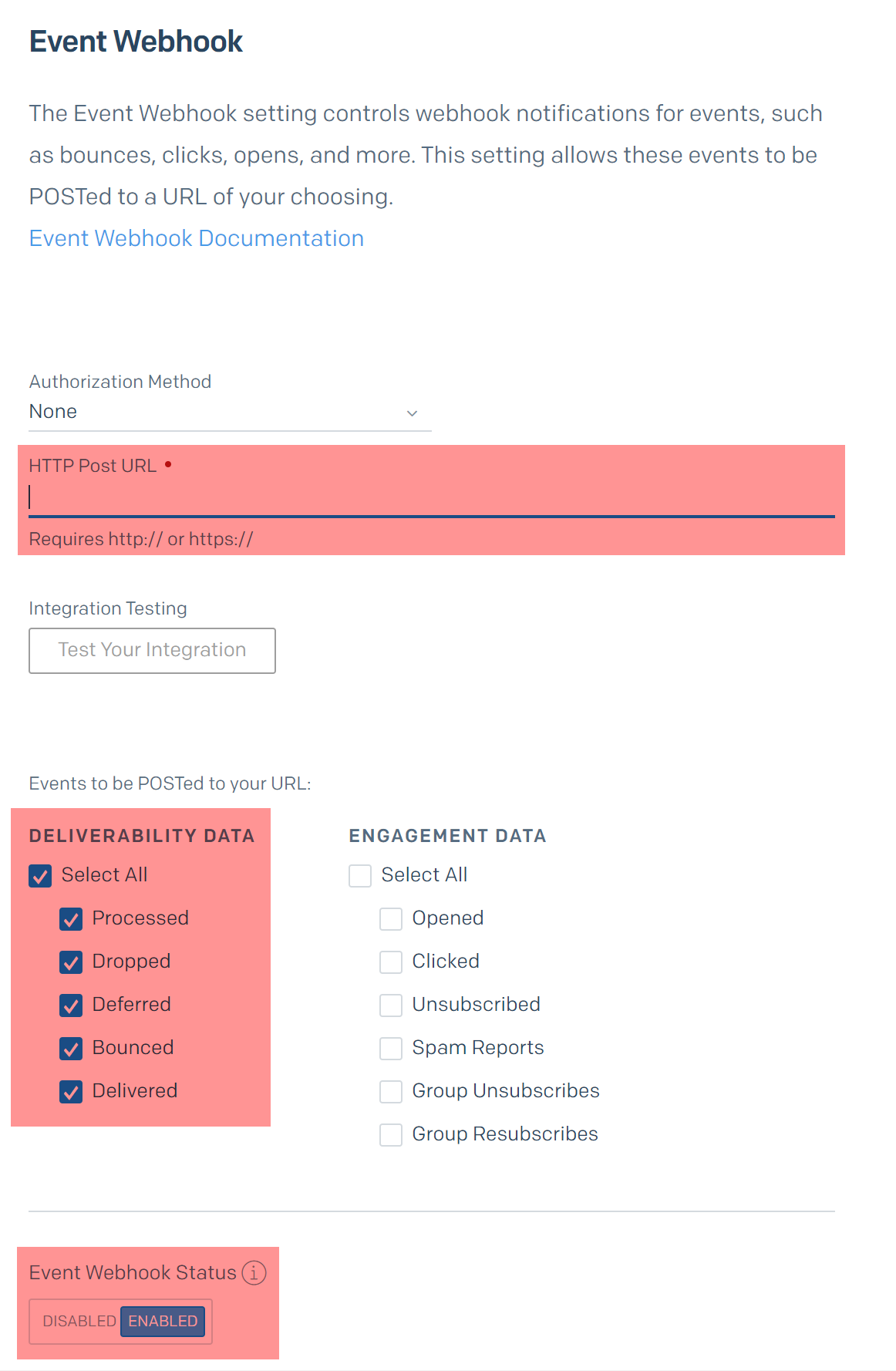
Configuration: HTTP Post URL
The URL entered for HTTP Post URL will depend on which type of callback service was configured:
-
Standard Callback Service:
http://<URL of Sendgrid Callback Server>/SendGridCallbackService/callbackservice.svc/<RPI Client ID> -
Web API Callback Service:
http://<URL of Sendgrid Callback Server>/postevents/<RPI Client ID>
Configuration: Deliverability data
Choose the event data to send via the web hook.
Some customers choose to disregard the Processed event to help reduce the amount of files to be processed by the callback service.
Configuration: Event webhook status
Toggle the switch to ENABLED and select Save once complete.
Callback service API endpoints
|
Endpoint |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
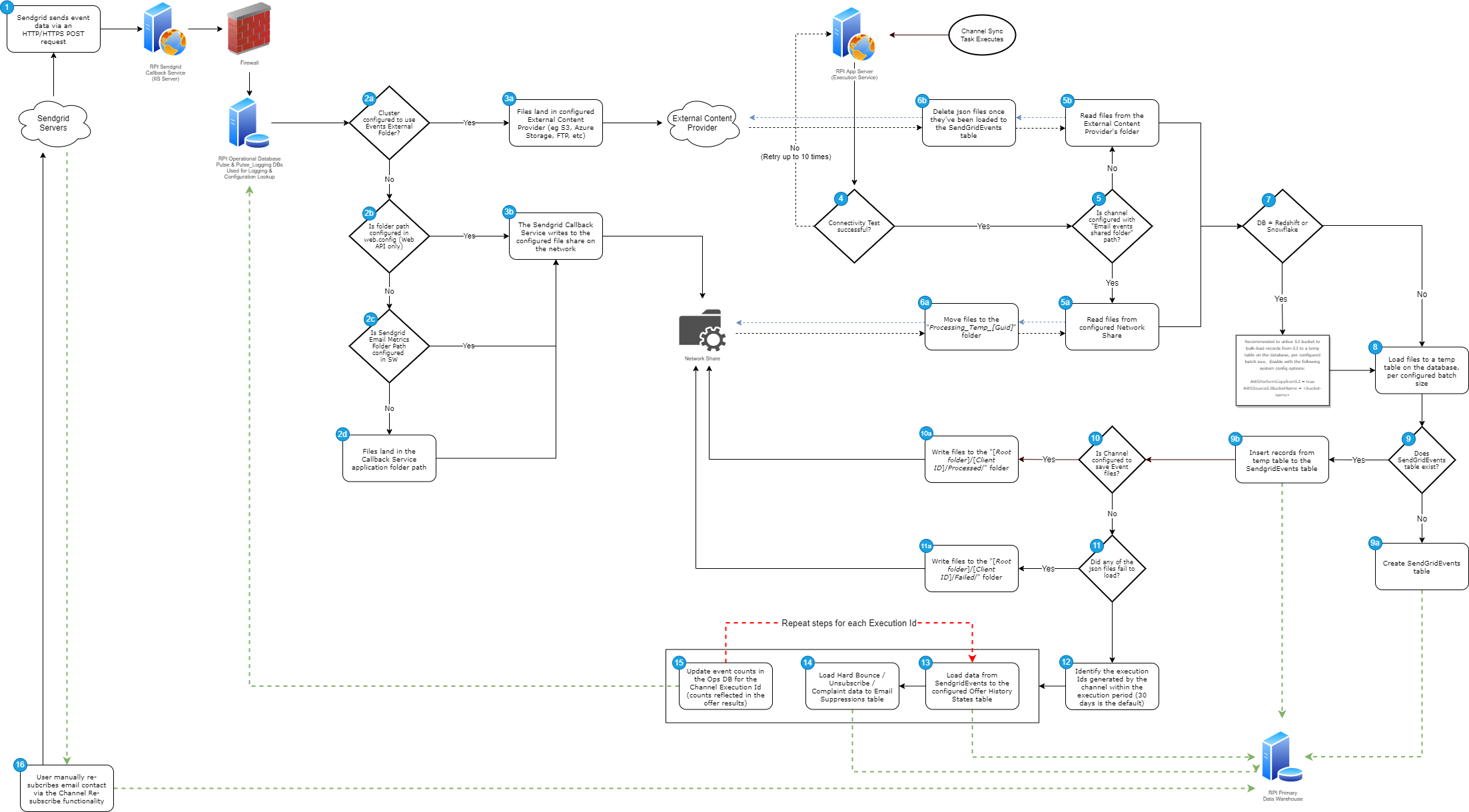
Callback Service: Inbound Process (Part 1)
-
As part of SendGrid's webhook functionality, new event data is sent via an HTTP/HTTPS POST request to an IIS server where the Callback Service is running.
-
Upon arrival of the new event data posted by SendGrid webhook, the callback service is going to:
-
First look for any external content provider settings configured at
SendGridWebAPIExternalContentProviderSettingson a cluster-level configuration, and the files will be posted to that respective location, or -
If no ECP is configured in the
SendGridWebAPIExternalContentProviderSettingssetting, the default email metrics folder path configured atemailMetricsFolderLocationsetting inweb.configfile will be used (if using the Web API Callback Service). -
However, if there is no folder path specified in
emailMetricsFolderLocationsetting, the callback service will try to look for a valid folder path configured atSendGridEmailMetricsFolderPathon a cluster-level configuration. -
If none of these are configured, the Callback service application folder path will used. The folder path is configured either on external content provider or on a local server that serves as the root folder where event data is saved.
-
Typically, an external ECP such as S3 is configured using SendGridWebAPIExternalContentProviderSettings, if there's a security requirement to utilize a cloud provider for receiving and storing the SendGrid event files. This option can be used with any database, not just Redshift and Snowflake.
-
Once the event data stream is available, it is read and stored as a
JSONfile either on:-
External content provider folder, or
-
On a specific network folder location that can be accessed by RPI Execution Service
The
JSONfile has the following standard file naming:[GUID]_Events.jsonand is always written into the folder location[Root folder]/[Client ID]/.[Client ID]is an RPI client ID represented as GUID value, and this folder is automatically created from the root folder if it doesn't exist yet. -
In the event of error, e.g. invalid root folder path or any folder permission related issues, the JSON file will be written into FailedEvents_[Client ID] folder under Callback service application root folder. This is to ensure that we are not losing any event data when an error has occurred. The FailedEvents_[Client ID] folder is automatically created if it doesn't exist yet. All JSON files stored in this folder can be used to reprocess the files. To reprocess, all JSON files must be manually copied and pasted into [Root folder]/[Client ID]/ folder. This process is applied either using an external content provider or local server folder locations. For external content provider, we recommend using any 3rd-party tool when copying files in bulk.
SendGrid channel synchronization task process (part 2)
Channel Sync Task
When a SendGrid channel is created in RPI, it will also create a "SendGrid Channel Synchronization" task that is scheduled to run every [x] period.
This task is responsible for ingesting the event files provided by SendGrid via their web hook process.
-
Channel Sync task is initiated, and it will first test connectivity to the Callback Service and the network share (if configured). If it fails, it will retry up to 10 times before the Channel Sync task is put into a failed state.
-
The task will determine the source folder location of
JSONfiles, based on what is configured within the SendGrid channel configuration settings:-
If "Email events shared folder" is configured, it will read the
JSONfiles from the configured Network share, or -
If "Events external folder" is configured, the
JSONfiles will be read and processed from the configured specific External content provider folder
-
-
If:
-
"Email events shared folder" is configured on the channel, a batch of the
JSONfiles are moved intoProcessing_Temp_[Guid]temporary folder on the network share. This is to ensure that no other clients with SendGrid channels can interrupt the processing operations of another client. After processing, the folder is deleted. -
"Events external folder" is configured, those
JSONfiles in external content provider folder are going to be deleted once the records have been imported intoSendGridEventstable successfully.
-
-
If the primary database is either Redshift or Snowflake, the recommendation is to use an S3 bucket to bulk load the records, for improved performance. If an S3 bucket is not configured, the process will only insert 200 records at a time. This can be enabled by updating the
AWSPerformCopyfromS3andAWSSourceS3BucketNamesettings in the tenant's system configuration.
This setting is not related to the SendGridWebAPIExternalContentProviderSettings setting in Server Workbench, which enables the option of having the SendGrid event files pushed directly to an S3 bucket, instead of a network share.
-
Once those
JSONfiles are available on specific folder location (either in "Events external folder" or "Email events shared folder"), these files are processed in batch, depending on the number of files set in Max import file count setting on SendGrid channel configurations. The default value of this setting is200. This means 200JSONfiles can be processed per batch per channel synchronization task execution. The value can be set to a higher value, but it may lead to poorer processing performance. Testing may be needed to find the ideal value for a particular environment.Processing
JSONfiles involves de-serializing each file and extract the required information such as:email,timestamp,event,category,sg_event_id,channelId,channelExecutionId, andclientId. This information will be imported into theSendGridEventstable. The records from theJSONfiles are imported in batch, depending on the number of record count set in Event import batch size option on SendGrid channel configuration. The default value is10,000, which means 10,000 records will be imported intoSendGridEventstable per batch.When Process older event files first option is selected on SendGrid channel configurations, it allows older
JSONfiles to be processed first. In this case, we can still retrieve those previous event data that were not processed successfully.
This option is not available on any RPI versions before v6.2.
-
Check if the
SendGridEventstable exists on the database:-
If it does not exist, the process will create the table when there's at least one execution
-
If the table exists, the process will insert the records from the temp table to the
SendGridEventstable
The
SendGridEventstable is used to store the original raw records from theJSONfiles. -
-
If the
SaveEmailEventsproperty is set toTrueon the channel configuration, theJSONfiles will be saved to the[Root folder]/[Client ID]/Processed/folder on the network share. These saved files can be used for troubleshooting purposes. -
In the event of an error during import of a batch of
JSONfiles intoSendGridEventstable, a copy ofJSONfiles is automatically generated and saved into theFailedfolder within the root folder configured in Email events shared folder. These files from theFailedfolder are commonly used for troubleshooting purposes and can be used re-importing to theSendGridEventstable. The SendGrid channel synchronization task will fail, and an error message will be reported back to user. -
When
JSONfiles have been processed and imported successfully intoSendGridEventstable, each fulfillment activity (Channel Execution) generated by a specific SendGrid channel will be processed accordingly. It always processes the most recent fulfillment activity against the records from theSendGridEventstable that matches the following criteria:-
SendGrid channel ID should match
ChannelIDvalue -
Channel execution's client id should match
ClientIDvalue -
Channel execution's
LastSynchronizationDatevalue must greater than or equal toEntryDatevalue
-
-
The channel execution's
LastSynchronizationDatefield is based onEntryDatevalue and is used to avoid calculating those records from theSendGridEventstable that were processed and imported already inoffer_history_Statetable. The default value of this field is set to1970-1-1 00:00:00in UTC and is always updated with the recentEntryDatevalue that matches the record fromSendGridEventstable. The records successfully matched will be inserted intooffer_history_Statetable. This process is repeatedly executed until all fulfillment activities are processed. -
Unsubscribes from the last 7 days are captured, and those collected records are written to the RPI email suppression table. The last [x] days frequency default value can also be modified through
importUnsubFrequencyparameter, which can be found in SendGrid channel synchronization task details XML value. -
The records from
offer_history_Statetable will be aggregated based on fulfillment state and channel execution Id to reflect each fulfillment state count in Offer activity result window. -
If applicable, a user can re-subscribe a contact if they've previously unsubscribed and were added to the Global Suppression list in SendGrid. This is done via the Re-subscribe functionality in the Channel configuration (General tab).
This functionality only supports the option to re-subscribe an email address if they've unsubscribed. It does NOT apply to email addresses that have hard bounced.
There are 3 steps to this process:
-
Execute a
GETon theSuppressions/Globalendpoint to determine if the email address is currently on the list. -
If
YES, then execute aDELETEon theSuppressions/Globalendpoint to remove the email address from Global suppression list. -
Finally, delete the email address from the
suppression_emailtable associated with the channel where the re-subscribe request is occurring.
Limitations
Known limitations
-
The API does not support the option to create “View as Web Page” links that mirror the email content.
-
The ability to schedule a delivery is not supported by their API.
-
Bypassing unsubscribes is not supported.
-
Asynchronous processing is not supported.
-
The use of social elements including Facebook Like Image and Facebook Like Share buttons are not supported.
-
The “Forward-to-Friend” option is not supported.
-
The use of content sharing for Facebook and Twitter is not supported.
Performance limitations
-
During the Outbound fulfillment, the Mail Merge process (noted in Step 4 of the diagram) is where we typically see the largest bottleneck in terms of performance.
-
Below are the average durations for the mail merge step, across different send volumes and databases. The duration will vary based on the number of personalization attributes included in the offer. These represent average execution times for an email blast with 5 personalization attributes:
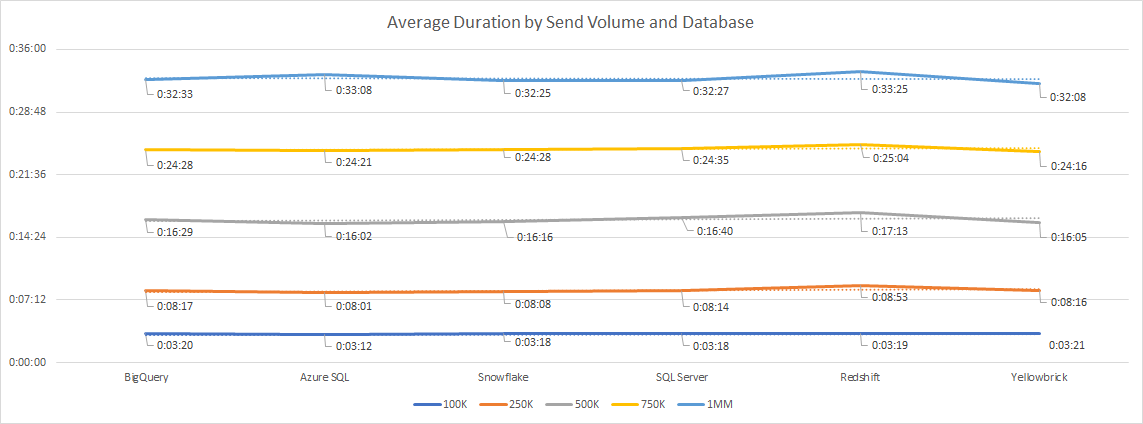
-
In April 2020, SendGrid deprecated their Segment functionality when calling the
Sendendpoint, which we previously utilized to render dynamic content.-
We modified the connector to accommodate for this change, but it resulted in slower performance when generating the mail merge files, particularly for offers that use dynamic content.
-
Several changes have been made to the connector that have significantly reduced that time, and the sending performance is similar to what it was before SendGrid deprecated the functionality.
-
Troubleshooting
When Enable trace option is selected at SendGrid channel configurations, the following samples of trace HTTP Request/Response log messages are being generated:
|
HTTP Request |
HTTP Response |
|---|---|
|
30/04/2021 3:12:33 pm
Version :6.3.0.0
Category: Plugin Trace
|
30/04/2021 3:12:34 pm
Raw Content:
Version :6.3.0.0
Category: Plugin Trace
|
|
30/04/2021 3:06:45 pm
Version :6.3.0.0
Category: Plugin Trace
|
30/04/2021 3:06:47 pm
Raw Content:
Version :6.3.0.0
Category: Plugin Trace
|
|
30/04/2021 3:06:47 pm
Version :6.3.0.0
Category: Plugin Trace
|
30/04/2021 3:06:47 pm
Raw Content:
Version :6.3.0.0
Category: Plugin Trace
|
|
|
30/04/2021 3:06:53 pm
Category: Plugin Trace
|
FAQs
Which API version should we use to configure the channel?
Given that SendGrid will eventually deprecate the v2 APIs, the recommendation is to use the v3 API where possible. SendGrid has not yet provided timing for when they will deprecate the v2 APIs.
Which Callback Service should we use to configure on the callback server - Standard or WebAPI?
Both versions provide the same functionality for processing event data, but the WebAPI version has an additional Status endpoint that will provide the status of the service, including the database connections.
Is the OfferHistory_States table suitable for reporting?
No, it's not recommended to use OHS for any reporting, primarily for two reasons:
-
Querying the OHS table may potentially impact processing of the Channel Sync tasks
-
The data in the OHS table is also deduped at the
rpcontactid,fulfillmentstate, andeventnamelevel, which may not provide the full context when analyzing campaign performance
Please use the SendGridEvents table to support reporting.
We’re missing data in the OfferHistory_States table. Is there a way to retroactively load the missing event data?
Yes, in the Interaction operational database, update the LastSynchronizationDate column in the op_channelExecution table for the channel executions that were impacted. The next time the channel sync task runs, it will use that new date to pick and process records from the SendGridEvents table.
Are there any SQL scripts available that could be used to manually load data to the OfferHistory_States table and update the operational table for the Offer Results counts?
Yes, the steps are covered in VSTS #12300 > https://redpointcmp.visualstudio.com/Interaction/_workitems/edit/12300
Using standard SendGrid Callback service, the events files are being written into default directory: C:\temp\RedPoint\SendGrid\ not on the directory configured in SendGridEmailMetricsFolderPath setting. What is best place to start looking at this issue?
The best place to start troubleshooting this issue is to check whether the standard SendGrid callback service is able to communicate with the Pulse operational database.
We’re experiencing a backlog in processing the event files. Are there any recommendations for improving overall performance when loading the files?
Yes, the following suggestions may help improve performance:
-
In the Channel config, increase the following thresholds:
-
Max Import File Count: to at least
20000, which will pick up and process up to 20000 files during each sync. -
Event batch import size: to
20000, which will process and load up to 20000 records during each sync.
-
-
For Redshift and Snowflake integrations, ensure the system configuration is setup to use an S3 bucket for bulk loading the records.
-
For customers using an EC2 instance for the callback server, they should consider having a minimum of 8GB of memory and storage type at the GP3 (or higher) tier, which supports higher IOPs (input/output operations per second).
-
In the SendGrid portal, uncheck any events that may not be necessary, such as
Processed.
Can I get access to a sandbox account that can be used for demos or trying out the connector on my local instance?
Yes, reach out to support@redpointglobal.com, and the team will provide the credentials.
Is configuring the SendGridWebAPIExternalContentProviderSettings setting required when using a Redshift or Snowflake database?
No, this setting can be used with any database. The only requirement for Redshift and Snowflake instances is to configure the AWSPerformCopyfromS3 and AWSSourceS3BucketName settings in the tenant's system configuration. This will improve performance by utilizing the COPY command to bulk load the data to the database.
The SendGridWebAPIExternalContentProviderSettings setting is typically enabled when there's a security requirement to utilize a cloud provider for receiving and storing the SendGrid event files.
Where are the Channel Sync and Offer Fulfillment activities logged and how can they be accessed by RPI users?
Channel Sync and Offer Fulfillment activities do not generate dedicated execution or audit logs within RPI. As a result, RPI users do not have direct access to detailed execution information. Operational visibility is limited to high-level workflow execution status and aggregate status counts, message delivery and event data persisted in the SendGridEvents table, and application-level error messages. No step-level execution details or SQL-level diagnostics are available.
Is it acceptable to reuse a ChannelExecutionID?
Reuse of ChannelExecutionID is supported and used on recurring workflows. Each fulfillment activity (Channel Execution) generated by the SendGrid channel is processed according to the following:
-
SendGrid channel ID should match
ChannelIDvalue -
Channel execution's client ID should match
ClientIDvalue -
Channel execution's
LastSynchronizationDatevalue must greater than or equal toEntryDatevalue
The system always processes the most recent fulfillment activity that meets these criteria.
How is indexing applied to key tables for workflow efficiency?
To ensure efficient processing of Channel Sync and Offer Fulfillment activities, key tables in the system are appropriately indexed. Indexing supports query performance and data retrieval for workflow execution.
SendGridEvents table:
-
Stores all event information related to SendGrid channels.
-
Primary key:
SGEventID -
Other columns include:
EntryDate,Event,Email,Category,Response,Attempt,Url,Status,Reason,Type,ChannelExecutionId,ChannelId,ClientId,Timestamp,IpAddress,UserAgent,SgMachineOpen

