Overview
Geocoding associates geographic coordinates with input addresses, letting you pinpoint locations and carry out geography-based analyses. The Geocoder tool converts a free-form address (first line and last-line) into a normalized form, with latitude and longitude, county and state FIPS code, and census tract and block number. Note that while the Geocoder tool performs a type of address standardization, the results are not CASS certified. If you require CASS certification, consider licensing Data Management's Standardize Address tool.
The Geocoder tool can produce any or all of the following outputs:
-
First-line address
-
Last-line address
-
Address number
-
Directional prefix
-
Street name
-
Street suffix
-
Directional postfix
-
Unit designator
-
Unit number
-
City
-
State
-
ZIP Code
-
State FIPS
-
County FIPS
-
Census tract
-
Census block
-
Latitude
-
Longitude
-
Directional prefix2
-
Street name2
-
Street suffix2
-
Directional postfix2
-
Match score
-
Geocoding result category code
-
Geocode result flags
All elements are formatted in uppercase letters.
Geocoder tool configuration parameters
The Geocoder tool has two sets of configuration parameters in addition to the standard execution options: input and output.
Input
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Delivery address |
Input field containing the postal address. |
|
Last line as |
Select Single field if city, state, and ZIP Code are contained in a single field, or City, State and ZIP if they are separate fields. This is optional and defaults to Single field. |
|
Last line address |
If Last line as Single field, the input field containing the City, State, and ZIP Code. |
|
City |
If Last line as City, State and ZIP, the input field containing the City. |
|
State |
If Last line as City, State and ZIP, the input field containing the State. |
|
ZIP |
If Last line as City, State and ZIP, the input field containing the ZIP Code. |
|
Share Geocoder library among tools |
If selected, Data Management uses a single shared Geocoder library even if there are multiple Geocoder tools. |
|
Use alternate Geocoder data directory |
If selected, loads the Geocoder database from a specified alternate location. |
Output
See Output field names and sizes.
Configure the Geocoder tool
-
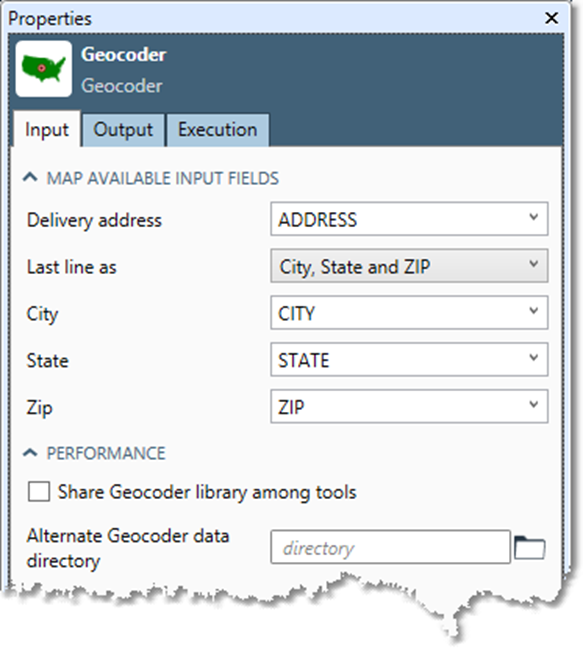
Select the Geocoder tool.
-
Go to the Input tab.
-
Select the Delivery Address box and select the input field that contains the first-line address. The first-line should be of the general form:
Number Predirectional Suffix Street_name Postdirectional Unit_designator Unit_number
Not all first-line address elements need be included. The following are all valid address first-lines:
4270 Evans Dr
123 S MAIN ST APT A
12E17N GERBER AVE
-
If necessary, use the Calculate tool to construct a first-line address from address components.
-
Select the Last line as box:
|
If |
Do this |
|---|---|
|
There is a single last line field |
Select Single field, and then specify the Last line address field. |
|
There is not a single last line field |
Select City, State and ZIP, and then select the City, State, and ZIP boxes to select the appropriate input fields. |
-
Optionally, you can select the Share Geocoder library among tools check box.
When Share Geocoder library among tools is selected, Data Management uses a single shared Geocoder library even if there are multiple Geocoder tools. Because the Geocoder library can be very resource-intensive, you should leave this set to the default "Share" setting unless you are explicitly replicating the Geocoder tool for parallel execution with a Splitter/Merge technique.
The Alternate Geocoder data library is specified for support and testing purposes only.
-
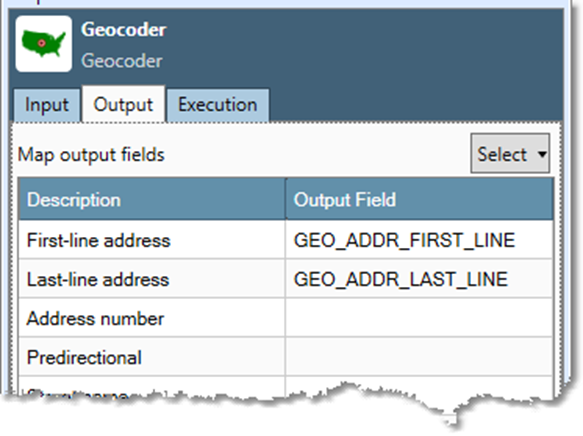
Go to the Output tab, and then map Output fields.
-
You can select the Select arrow and choose All, None, or Typical to generate default Output field names.
-
If desired, select any box in the Output field grid to change or delete that output field name, or map the output to an existing field.
Data Management automatically creates output fields, using the names and the sizes listed below. If you choose to map the output fields to fields that already exist in the input file, the fields must be large enough to handle the standard size of the components as specified in the table below., or results may be truncated.
|
Output field |
Description |
Default type & field size |
|---|---|---|
|
|
All of the first-line address components |
VarText 64 |
|
|
All of the last-line address components |
VarText 64 |
|
|
The address number component of the address |
VarText 10 |
|
|
The directional prefix component of the address |
VarText 2 |
|
|
The street name component of the address |
VarText 28 |
|
|
The street suffix component of the address |
VarText 4 |
|
|
The directional postfix component of the address |
VarText 2 |
|
|
The unit designator component of the address |
VarText 4 |
|
|
The unit number component of the address |
VarText 8 |
|
|
The city name |
VarText 28 |
|
|
The state abbreviation |
VarText 2 |
|
|
The ZIP code |
VarText 5 |
|
|
The state FIPS code |
Three-digit integer |
|
|
The county FIPS code |
Two-digit integer |
|
|
The Census tract code |
VarText 6 |
|
|
The Census block code |
VarText 4 |
|
|
The latitude |
Double-precision float |
|
|
The longitude |
Double-precision float |
|
|
The directional prefix component of the second street for intersections only |
VarText 2 |
|
|
The street name component of the second street for intersections only |
VarText 28 |
|
|
The street suffix component of the second street for intersections only |
VarText 4 |
|
|
The directional postfix component of the second street for intersections only |
VarText 2 |
|
|
The match score |
Four-digit integer (0-1000) |
|
|
The address-coding result type |
One-character code |
|
|
The address-coding result flags |
Ten-character code |
-
Optionally, go to the Execution tab, and then set Web service options.
Address First-lines and Last-lines
The Geocoder tool requires that input addresses be of the form first-line/last-line. If your database contains addresses that are already parsed into components, you'll need to reassemble the components into composite fields using the Calculate tool.
As an example, the expression below creates a first-line address out of components (your component field names will be different). Note the spaces inserted between components.
ADDR_NUM + " " + PREDIR + " " + ST_NAME + " " + SUFFIX + " " + POSTDIR + " " + UNITDES + " " + UNIT
Make sure the composite fields are at least 48 characters long or they may be truncated.
Match scores
Match quality is expressed as a score between 0 and 1000. Higher scores indicate greater confidence in the match of the street record to one in the geocoding database. Match scores are used to define Match thresholds (the match score that must be achieved to count as a match) and Multiple thresholds (the minimum distance allowed between the scores match candidates before the multiple match flag is set).
Result Category codes
The Result Category describes the type of geocode applied to a record.
|
Result Category |
Description |
|---|---|
|
A |
Address-level coding |
|
5 |
Zip5 level coding |
|
I |
Intersection coding |
|
F |
Coding failure |
Result Flag codes
The Result Flags describe the disposition of a geocoded record.
|
Result Flag |
Description |
|---|---|
|
M |
There are multiple candidates that cannot be distinguished |
|
0 |
The street pre-directional was added or changed |
|
1 |
The street name was added or changed |
|
2 |
The street suffix was added or changed |
|
3 |
The street post-directional was added or changed |
|
4 |
The address number was out of range |
|
5 |
A letter of the address number was moved to the unit number |
|
6 |
City was added or changed |
|
7 |
State was added or changed |
|
8 |
Zip was added or changed |

