Overview
The JSON Output tool reads a relationally-linked set of records from multiple inputs, and writes JSON-formatted documents as one or more fields or files. Each input record type has an ID field and (except for the root record type) a parent ID field. The tool links together records at each level in the hierarchy by joining the ID fields of parent records to the "parent ID" field of child records, producing a JSON document for each input "root" record. Thus, the input records must meet the following requirements:
-
Each ID is unique
-
Each parent ID refers to a valid parent record
When a JSON Output tool is used to generate a document with three or more levels of linkage, the intermediate levels must be globally sequenced by {parentID,itemID}. This is because the JSON Output tool performs a streaming join on all inputs simultaneously, so the linkage keys must all be globally ordered on both sides of every implied join.
Intermediate sorting
This section provides information about intermediate sorting for multiple root records with deep child nodes.
The JSON Output tool performs a join simultaneously on all inputs using the linkage fields. At each child level, the parentID of the child record (designated by the ## Path) is joined to the ID of the child (designated by the # Path). The JSON Output tool does not sort the inputs. These must already be globally ordered on the linkage keys. This is easy when you have two levels: order the root records by their ID, and order the child records by the root ID.
However, when there are three or more levels, ordering becomes more complicated.
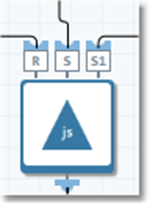
In the case shown above, the middle child record "sub1" is linked as follows.
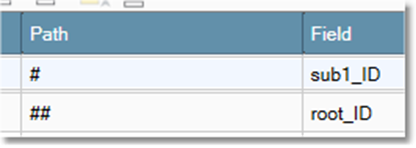
The grandchild record "sub2" is linked as follows.
Because the child record sub1 is linked to both the root and sub2, it must be globally ordered on both root_ID and sub1_ID. In practice, this means that you must renumber the ID values of sub1 to produce a correctly-ordered table, and then apply the same renumbering to the sub1_ID field of the sub2 records to preserve the correct linkage.
If you order sub1 by its parent's ID, its own ID may be out of order (for example {1,3,5,2,4,6}). This will break the join to the grandchild sub2. Instead, use an upstream Number Records tool to renumber sub1 to {1,2,3,4,5,6}, and then extract an {oldID, newID} table: {{1,1},{3,2},{5,3},{2,4},{4,5},{6,6}}.
Join this renumber table to the sub2 records, and rename the join output fields to produce the new parent ID instead of the old parent ID.
If there are more than three levels in the JSON, this renumbering process cascades down each level.
JSON Output tool configuration parameters
The JSON Output tool has several sets of configuration parameters in addition to the standard execution options.
Configuration
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Output to |
The destination of the data:
|
|
Output file |
If Output to is File, the output file name. |
|
Open file time |
Specifies when the output file will be opened:
|
|
Write empty file if no records are read
|
If selected, writes an output file or field even when no records are read. This is unavailable if Open file time is When project is started. |
|
Output field |
If Output to is Field, the field to which the data will be written. |
|
Include input fields |
If Output to is Field, optionally passes through the "extra" input fields to the "root" record. This can be useful in certain kinds of processing where it is desirable to carry through identifying information that is not represented in the JSON documents. |
|
Multi-doc mode |
How to write output files or fields that may contain multiple JSON documents:
See Multi-doc mode for full details. |
|
Use repository schema |
If selected, configure the field layout using the specified Schema instead of configuring fields directly. |
|
Schema |
If Use repository schema is selected, a schema must be specified. |
|
Record |
Record specification defining an output of the tool. This is difficult to configure manually. See Configuring the JSON Output tool. |
|
Path |
Sequence of identifiers separated by |
|
Replication factor |
Number of copies of each block that will be stored (on different nodes) in the distributed file system. The default is |
|
Block size (MB) |
The minimum size of a file division. The default is |
Options
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Unmapped element treatment |
Specifies how to handle fields that are mapped in the Record section, but do not exist on the input connector at configuration time. (This can occur in macros, for example.) Choose…
|
|
Missing field treatment |
Specifies how missing fields are handled. Choose…
|
|
Omit empty attributes |
If selected, suppresses blank attributes. |
|
Omit empty elements |
If selected, suppresses blank elements. |
|
Format for readability |
If selected, formats JSON output with newlines and spaces are added to make readable indentation. |
Configure the JSON Output tool
The procedure for configuring a JSON Output tool depends on the data target.
|
If the data target is... |
Do this |
|---|---|
|
A file or files |
|
|
A field or datastream |
...to write files
To configure the JSON Output tool to write files:
-
Select the JSON Output tool.
-
Go to the Configuration tab on the Properties pane.
-
Select Output to and choose File, and then specify the output file and format.
|
If you have... |
Do this |
|---|---|
|
A file containing JSON-formatted records in the desired schema. |
Specify the name of the file, select Analyze The file you specify will be overwritten. |
|
A JSON schema for this file already defined in the repository. |
Specify the name of the output file. Select Use repository schema, and select the schema from the drop-down list. |
|
Neither a file containing JSON-formatted records in the desired schema, nor predefined repository schema. |
Select the Analyze tab and enter a formatted sample of the expected JSON input. Select Analyze |
-
Optionally, specify Open file time.
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Default |
Use the site/execution server setting. If you select this, you can optionally select Write empty file if no records are read. A warning will be issued if the tool setting conflicts with the site/execution server setting. |
|
When project is started |
Open output file when the project is run. |
|
When the first record is read |
Open output file when the first record is read. If you select this, you can optionally select Write empty file if no records are read. |
|
After the last record is read |
Output records are cached and not written to the output file until the tool receives the final record. If you select this, you can optionally select Write empty file if no records are read. |
-
Optionally, select Write empty file if no records are read if selected to write an output file even when no records are read. This option is unavailable if Open file time is When project is started.
-
Optionally, specify Multi-doc mode:
-
Document per file: (default) each output file contains a single JSON document.
-
Document per line: each output file contains multiple JSON documents, with one document per line of text.
-
-
Select Commit

-
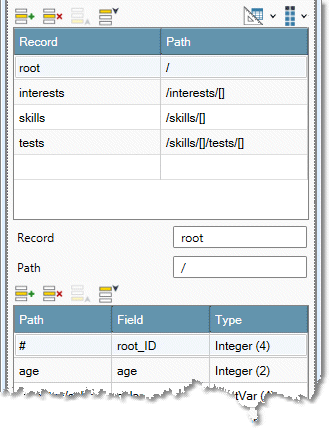
Select each cell in the Record column, and examine the Fields grid to verify that the schema is correct and the data is accurately described.
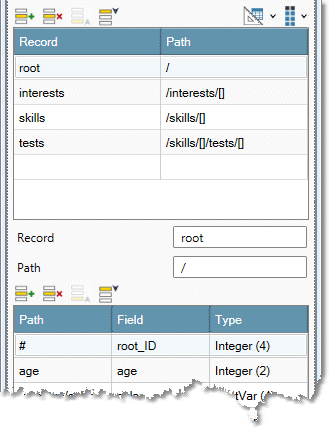
-
Select the Options tab to tune the JSON output format.
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Unmapped element treatment |
Specifies how to handle fields that are mapped in the Record section, but do not exist on the input connector at configuration time. Options are:
|
|
Missing field treatment |
Specifies how missing fields are handled. Options are:
|
|
Omit empty attributes |
If selected, suppresses blank attributes. |
|
Omit empty elements |
If selected, suppresses blank elements. |
|
Readability |
Formats JSON output with newlines and spaces are added to make readable indentation. |
-
Optionally, go to the Execution tab and Enable trigger output, configure reporting options, or set Web service options.
...to write fields
To configure the JSON Output tool to write fields:
-
Select the JSON Output tool.
-
Go to the Configuration tab on the Properties pane.
-
Select Output to and choose Field.
-
Select Commit to display the output connector, and then connect the desired target tool.
-
Select the Output field to which the data will be written, and then define the output format.
|
If you have... |
Do this |
|---|---|
|
An JSON schema for this file already defined in the repository. |
Select Use repository schema, and select the schema from the drop-down list. |
|
No schema defined for this file. |
Select the Analyze tab and enter a formatted sample of the expected JSON input. Select Analyze |
-
Optionally, select Include input fields to output all input fields.
-
Optionally, specify Multi-doc mode:
-
Document per file: (default) each output field contains a single JSON document.
-
Document per line: each output field contains multiple JSON documents, with one document per line of text.
-
-
Select Commit

-
Select each cell in the Record column, and examine the Fields grid to verify that the schema is correct and the data is accurately described.
-
Select the Options tab to tune the JSON output format.
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Unmapped element treatment |
Specifies how to handle fields that are mapped in the Record section, but do not exist on the input connector at configuration time. Options are:
|
|
Missing field treatment |
Specifies how missing fields are handled. Options are:
|
|
Omit empty attributes |
If selected, suppresses blank attributes. |
|
Omit empty elements |
If selected, suppresses blank elements. |
|
Readability |
Formats JSON output with newlines and spaces are added to make readable indentation. |
-
If you specified the Use template option in the previous step, select the Template tab and enter an XML example of the output document format which contains default values for the unmapped or missing elements.
-
Optionally, go to the Execution tab and Enable trigger output, configure reporting options, or set Web service options.

